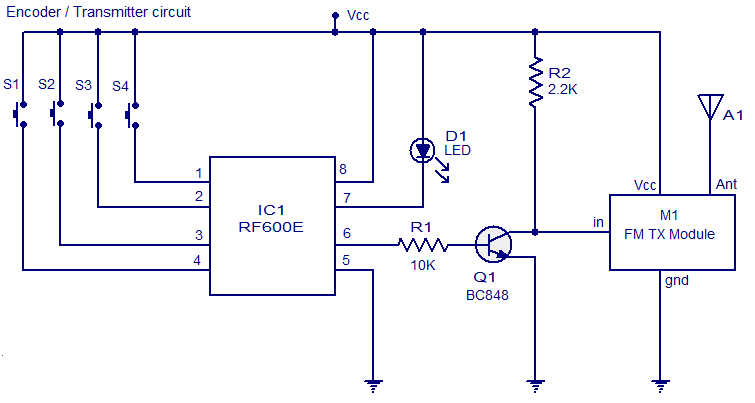
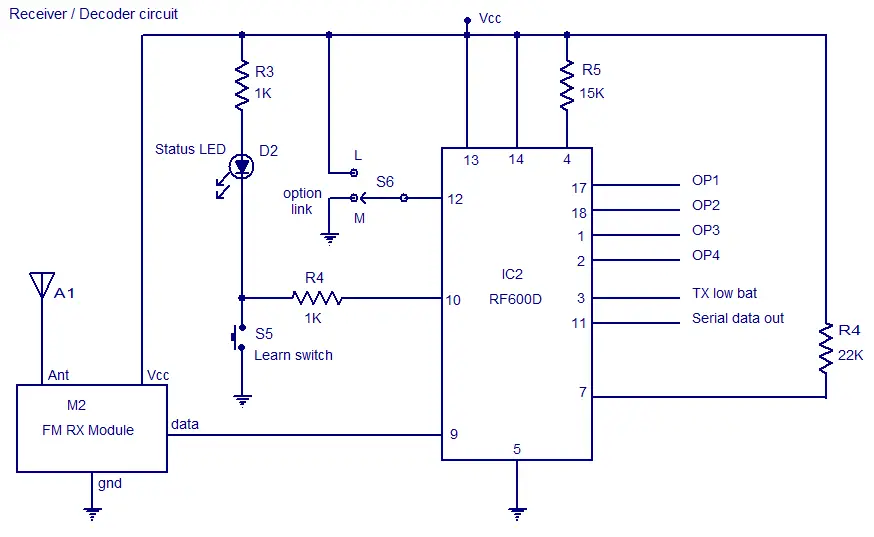
LONG RANGE FM TRANSMITTER ELECTRONIC DIAGRAM
This circuit works optimally by adding RF amplifier and antenna. Here is the schematic diagram :
Parts list :
- Diode D1 : BB109
- Resistor R1 : 10k ohm
- Resistor R2 : 100k ohm
- Resistor R3 : 180k ohm
- Resistor R4 : 4K7
- Resistor R5 : 15k ohm
- Resistor R6 : 68 ohm
- Resistor R7 : 470 ohm
- Resistor R8 : 39k ohm
- Resistor R9 : 10 ohm
- VR1 : 47k ohm
- VR2 : 22 ohm
- Capacitor C1-C3, C8 : 0.1 uF
- Capacitor C4 : 4.7 pF
- Capacitor C6 : 0.01 uF
- Capacitor C7 : 5.6 nF
- Capacitor C9 : 100 pF
- Transistor T1: BF494
- Transistor T2:2N3866
- Trimmer VC1-VC2 : 50p
- L1 : 4 round 20 cables SWG in plastic with 8mm diameter
- L2 : 2 round 24 cables SWG
- L3 : 7 round 24 cables SWG in plactic with 4mm diameter
- L4 : 7 round 24 cables SWG in ferrid bead